Mechanical Bike Disc Brakes: Ultimate Stopping Power
As an affiliate, we may earn from qualifying purchases. We get commissions for purchases made through links on this website. You can read more on our Affiliate Disclaimer here.
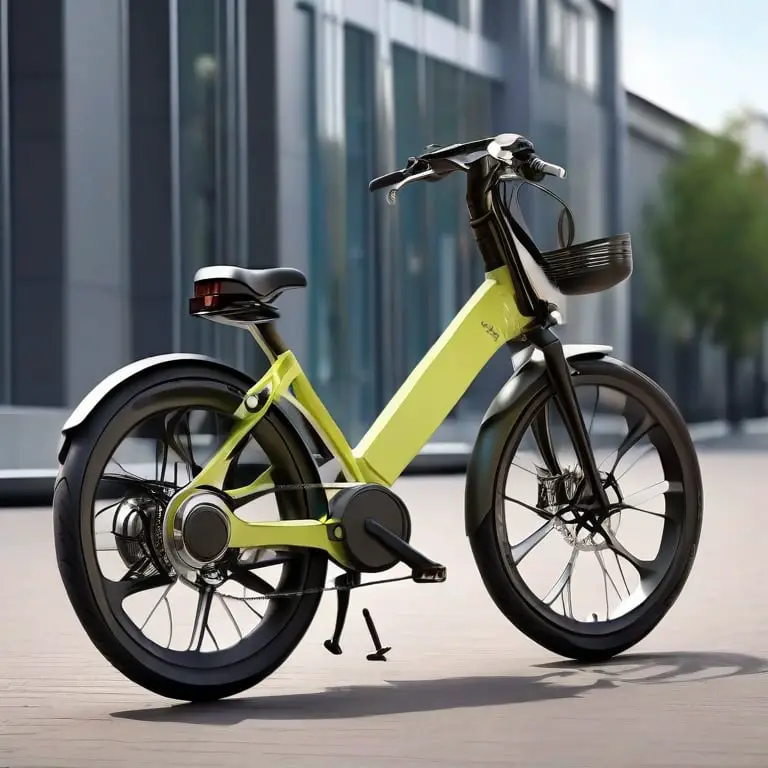
What is mechanical bike disc brakes? Mechanical disc brakes provide consistent stopping power for bicycles. They operate through a cable system to actuate the brake calipers.
Mechanical disc brakes, essential for modern cycling safety, enhance control and performance in diverse conditions. Compared to their rim brake counterparts, these braking systems offer superior stopping power, especially in wet or muddy environments where rim brakes may falter. By using a metal disc, or rotor, attached to the wheel hub, mechanical disc brakes generate friction with brake pads, leading to a controlled and efficient deceleration.
This setup minimizes brake fade during prolonged usage, such as on steep descents, ensuring reliable function over time. Cyclists of all levels appreciate the maintenance ease, with straightforward pad adjustments and cable replacements that require minimal tools. Affordable and durable, mechanical disc brakes continue to be a popular choice for both casual riders and serious enthusiasts seeking a dependable braking solution.

Credit: www.ridecyclery.com
Evolution Of Disc Brakes In Biking
The introduction of disc brakes to the world of cycling marked a significant turning point in how bikes were designed, built, and ultimately, how they perform. Unlike their rim brake counterparts, disc brakes brought about a new era of stopping power and reliability that was previously unheard of in the biking industry. Let’s delve deeper into the progression of this groundbreaking technology and its impact on cyclists around the globe.
Early Adoption In The Biking Industry
In the late 1990s, disc brakes began to surface in the biking world, initially gaining popularity within the mountain biking community. Their early adoption was propelled by the disc brake’s ability to perform consistently in diverse and challenging terrains. Unlike rim brakes, disc brakes are located at the center of the wheel, which shielded them from mud, water, and debris—elements that typically impaired rim brake function.
- 1997: First commercial mountain bike equipped with hydraulic disc brakes released.
- Early 2000s: Cross-country and downhill bikers fully embraced disc brakes for superior control.
- 2009: UCI legalizes the use of disc brakes in professional road bike races, fostering wider adoption.
Rapid improvements and innovations led to lighter, more compact, and even more efficient disc brake systems, sealing their place as the go-to choice for bike manufacturers and riders alike.
Advantages Over Traditional Rim Brakes
So why did disc brakes gain such a foothold over traditional rim brakes? The advantages are clear and significant:
| Disc Brakes | Rim Brakes |
|---|---|
| More consistent stopping power in all weather conditions | Performance can deteriorate in wet and dirty conditions |
| Less affected by heat build-up during prolonged braking | Can suffer from heat-induced fade and rim damage |
| Braking force does not diminish with wheel trueness or tire problems | Brake performance can be significantly impacted by wheel wobble |
| Longer lasting brake pads and less frequent maintenance | Pads may require more frequent replacements; rims can wear down |
- Improved Safety: Disc brakes provide more predictable performance, especially in descent and high-speed scenarios, giving riders a better sense of security.
- Compatibility with Wider Tires: As the cycling industry moves towards wider tires, disc brakes accommodate this trend without the clearance issues that rim brakes face.
- Aesthetic and Aerodynamic Advantage: With the braking mechanism removed from the rim, bike designs have become sleeker, with some disc brake configurations offering aerodynamic gains.
Indeed, the disc brake revolution has reshaped the biking industry by dramatically improving rider control, confidence, and comfort. As technology continues to progress, disc brakes remain at the forefront, continually innovating to meet the dynamic demands of modern cyclists.
Components Of Mechanical Bike Disc Brakes
Understanding the intricate components of mechanical bike disc brakes is essential for cyclists seeking efficient stopping power and safety on their rides. From the precise mechanism that clamps the rotor to the type of brake pads utilized, each component plays a pivotal role in the bike’s braking performance. Exploring the distinctions between cable actuated and hydraulic systems further unveils the technical diversity within the world of disc brakes. Let’s delve into the mechanics and materials that make up these essential parts of your bike.
Rotor And Caliper Mechanisms
The heart of the disc braking system lies within the rotor and caliper mechanisms. The rotor is a metal disc attached to the wheel hub that rotates with the wheel. When the brake is applied, the caliper—which is mounted to the frame or fork of the bike—activates brake pads to create friction against the rotor, thereby slowing the bike down. This vital interplay between components ensures smooth and precise braking.
Brake Pads And Their Materials
Brake pads are the critical contact points where the force is applied to slow down the bike. The effectiveness of braking largely depends on the materials used in these pads. Most mechanical bike disc brakes feature pads made from either organic, semi-metallic, or sintered compounds, each with unique advantages:
- Organic pads are known for their quiet operation and softer feel.
- Semi-metallic pads offer a balance between durability and performance.
- Sintered pads, made with metal particles, provide excellent performance in wet and harsh conditions.
Cable Actuated Vs. Hydraulic Systems
Mechanical bike disc brakes can be classified into cable actuated systems and their cousin, the hydraulic systems. Cable actuated, or mechanical, systems use a physical cable to transmit the force from the brake lever to the caliper. These systems are simple to maintain and are often more budget-friendly.
In contrast, hydraulic disc brakes operate by using fluid to transfer the force, resulting in more powerful and consistent braking, especially under heavy use or inclement weather conditions. Below is a quick comparison:
| System Type | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Cable Actuated |
|
|
| Hydraulic |
|
|
Performance And Maintenance Tips
Your bike’s disc brakes are the powerhouse of precise stopping and smooth riding. But like any finely-tuned system, they require regular checks and upkeep to operate at their best. Follow these expert tips to maintain optimal brake performance and longevity, ensuring you can rely on your brakes when you need them most.
Ensuring Consistent Brake Performance
Stellar brake performance is critical for safe and enjoyable rides. To ensure your brakes respond well every time, start by checking the brake pads for wear and tear. Replace them if you notice they’re getting thin or if you hear unusual noises during braking. Also, ensure the rotor surface is clean and free from oil or debris, which can impact braking efficiency.
- Inspect brake pads regularly for optimal thickness.
- Clean rotors with a specialized brake cleaner.
- Check for even pad wear to avoid uneven braking.
Adjusting And Aligning Disc Brakes
Proper adjustment is key to avoiding brake rub and ensuring smooth engagement. To adjust mechanical disc brakes, first loosen the caliper mounting bolts. Squeeze the brake lever to allow the caliper to center and then re-tighten the bolts. Check that the brake pads are parallel to the rotor for maximum contact and control.
| Step | Action |
|---|---|
| 1 | Loosen caliper bolts. |
| 2 | Engage brake lever. |
| 3 | Tighten bolts while maintaining lever pressure. |
| 4 | Check pad alignment and adjust as necessary. |
Proper Maintenance Practices For Longevity
To prolong the life of your disc brakes, routine maintenance is non-negotiable. Keep the brake system clean, including the levers and cables, to prevent dirt build-up, which can lead to poor performance. Regularly lubricate the cable system to ensure smooth operation and prevent corrosion. When you replace brake pads, take the opportunity to also inspect and service the caliper pistons and rotors.
- Clean all brake components with appropriate solvents.
- Lubricate moving parts lightly with a water-resistant lubricant.
- Replace cables and housings if they’re frayed or rusty.
- Periodically remove and clean the rotor to maintain flatness and remove contaminants.
Pros And Cons Of Mechanical Disc Brakes
Mechanical disc brakes are a crucial component for any cycling enthusiast, offering improved stopping power and performance over traditional rim brakes. However, they come with their own set of advantages and drawbacks that riders need to consider. In this section, we’ll delve into the pros and cons of mechanical disc brakes, assessing their efficacy across different terrains, how they cater to varied biking styles, and how they stack up against their hydraulic counterparts.
Advantages In Diverse Terrain
Mechanical disc brakes excel in diverse terrain conditions, offering consistent stopping power regardless of weather. This is because the braking surface is located away from the rim and closer to the hub, which is less likely to be exposed to water, mud, or debris. Such advantages include:
- Better performance in wet and muddy conditions, as the brake pads engage a rotor that is less susceptible to the elements.
- Less wear on the wheel, since the braking action does not directly affect the rims, allowing for prolonged wheel life.
- Compatibility with wider tires, which is particularly advantageous for off-road bikes that require more grip and stability.
Considerations For Different Biking Styles
Cycling is not one-size-fits-all, and neither are mechanical disc brakes. Certain biking styles may benefit more from their attributes while others could find them less practical. Some considerations include:
| Biking Style | Considerations for Mechanical Disc Brakes |
|---|---|
| Mountain Biking | Advantageous for reliable stopping power on steep, technical trails. |
| Road Cycling | May not be necessary for calm, dry terrains where lightweight caliper brakes suffice. |
| Touring | Beneficial for long distances with variable weather and loaded bike weight. |
| Urban Commuting | Useful for frequent stops and unpredictable urban environments. |
Comparison With Hydraulic Disc Brakes
When comparing mechanical disc brakes to hydraulic disc brakes, distinct differences influence a rider’s choice. Mechanical systems use cables and are generally easier and less expensive to maintain. For instance:
- Lower maintenance costs owing to the mechanical nature of cable-driven systems that don’t require bleeding or fluid replacement.
- Ease of field repairs, since mechanical systems can often be fixed with basic tools without specialized knowledge.
However, they also tend to be less efficient than hydraulic brakes, requiring more hand force to achieve similar stopping power. Additionally:
- Mechanical systems can struggle with uniform pad wear, leading to suboptimal braking efficiency over time.
- Adjustments may be needed more frequently due to cable stretch and pad wear.
Choosing The Best Mechanical Disc Brake System
Mechanical disc brakes have become the standard for a broad range of bicycles, from urban commuters to off-road adventurers. A perfect blend of efficiency, reliability, and performance, mechanical disc brake systems offer stopping power far superior to traditional rim brakes. Whether tackling steep hills, navigating through rainy conditions, or simply enjoying a leisurely ride, having a top-notch brake system is a non-negotiable for any serious cyclist. Let’s dive into what to consider when selecting a mechanical disc brake system that fits your needs and some well-regarded options cyclists swear by.
Factors To Consider Before Purchase
Choosing the right mechanical disc brake system requires careful consideration of several key factors:
- Compatibility: Ensure the brakes are compatible with your bike’s model and wheel size.
- Rotor Size: Depending on your riding style, choose the appropriate rotor size for optimal braking power.
- Adjustability: Look for systems that are easy to adjust for precision braking.
- Maintenance: Evaluate how easy the system is to maintain, including pad replacement and cable tension adjustments.
- Weight: Consider the weight of the brake system as it can impact your bike’s handling.
- Brake Pads: Check the type of pads used and their availability for future replacements.
- Brand Reputation & Reviews: Research and read reviews to gauge the reliability and performance of the system.
Top-rated Mechanical Disc Brake Systems
Some of the leading mechanical disc brake systems that have garnered high praise from both users and experts:
| Brand | Model | Features |
|---|---|---|
| TRP | Spyre SLC | Dual-sided actuation, lightweight, excellent modulation |
| Avid | BB7 | Built for durability, easy to maintain, versatile |
| Shimano | BR-CX77 | Reliable in adverse conditions, consistent performance |
Insider Tips From Biking Experts
Biking professionals and enthusiasts often share these insights concerning mechanical disc brakes:
- Always break in new brake pads to ensure peak performance.
- Regular maintenance is key – clean and inspect your brake system periodically.
- Adjust the cable tension appropriately; too tight or too loose can both affect braking efficiency.
- Consider the type of riding you do – some systems are better suited for aggressive mountain biking than for city commuting.
- Invest in quality brake rotors and pads – they can significantly enhance your bike’s braking capability.
Frequently Asked Questions For Mechanical Bike Disc Brakes
How Do Mechanical Disc Brakes Work?
Mechanical disc brakes function by a cable-activated lever forcing a caliper to press brake pads against a disc rotor. This creates friction, slowing the bike.
Are Mechanical Disc Brakes Better Than Rim Brakes?
Mechanical disc brakes offer superior performance in wet and dirty conditions. They provide consistent stopping power compared to rim brakes, especially on mountain or cyclocross bikes.
What Maintenance Do Mechanical Disc Brakes Need?
Regular maintenance includes cleaning the rotor, checking pad wear, and ensuring the brake cable is properly adjusted. Replace pads when worn and lubricate the cable periodically.
How To Adjust Mechanical Bike Disc Brakes?
Adjusting mechanical disc brakes involves aligning the calipers, setting the pad distance, and tensioning the brake cable. Use tools like Allen keys and cable pullers for precise adjustments.
Conclusion
Understanding the mechanics of bike disc brakes enhances riding safety and performance. Embracing their benefits will contribute greatly to your cycling experience. Ensure regular maintenance for optimal function. Ready to upgrade? Choose disc brakes for a reliable, efficient ride. Stay informed, stay safe, and enjoy the journey.

Steven is a professional cyclist and his passion is cycling. He has been cycling for the last 6 years and he loves using bikes while outing as well. Based on his experiences with the different types of bikes; he is sharing his opinions about various bikes so that a beginner can start right away. Find him on Twitter @thecyclistguy Happy Biking.